Contents
% /home/dimarzio/Documents/working/12229/lectures/alias.m % Sat Nov 11 14:19:11 2017 % Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University
Setup
npts1=2^16; npts=2^4; t=[0:npts-1]*10e-3/npts; % Time axis % Sampling Frequency dt=t(2)-t(1) fsample=1/dt
dt =
6.2500e-04
fsample =
1600
Generate the signal
Start with two sinusoidal waves
f1=400; omega1=2*pi*f1; f2=1000; omega2=2*pi*f2; vm1=0.025;phi1=30*pi/180;v1=vm1*cos(omega1*t+phi1); vm2=0.05;phi2=65*pi/180;v2=vm2*cos(omega2*t+phi2); vsignal=v1+v2; % Add some random noise vn=0.005;vnoise=randn(size(t))*vn; % Smaller than fftclass.m % Why so little noise? Smaller number of points in the FT. v=vsignal+vnoise; th=[1:npts1]*10e-3/npts1; % Time axis for high sample rate vh1=vm1*cos(omega1*th+phi1); vh2=vm2*cos(omega2*th+phi2); vhighsample=vh1+vh2;
Plot vs. time
figure;plot(t,v,'-bo',t,vsignal,'r-x',th,vhighsample,'c');grid on; xlabel('t, Time, sec');ylabel('Signal Volts'); % Just the high frequency term figure;plot(t,v2,'-bo',th,vh2,'c');grid on; xlabel('t, Time, sec');ylabel('Signal Volts'); % Note that we missed four cycles out of 10. Not surprising if we % see this 1000Hz signal at 600Hz in the Fourier Transform.
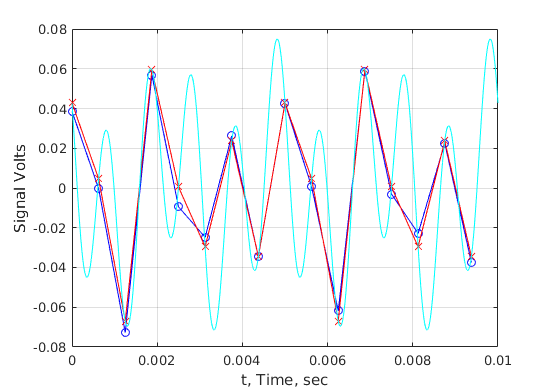
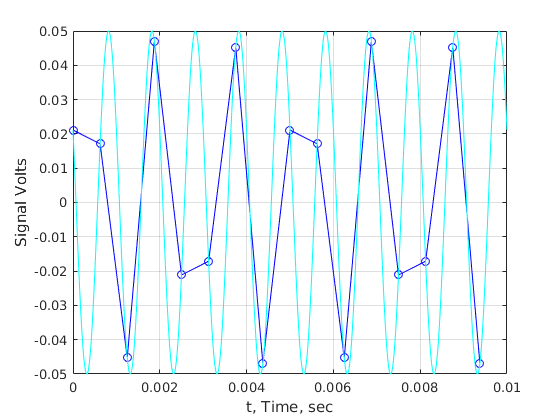
Fourier transform
Vsignal=fftshift(fft(vsignal)/npts*max(t));
V=fftshift(fft(v)/npts*max(t));
f=fftaxisshift(fftaxis(t)); % needs 2 functions from Chuck DiMarzio
plot the spectra
test=find(abs(f)<5*max(f1,f2)); % Noise-free signal figure;plot(f(test),real(Vsignal(test)),'b-o',... f(test),imag(Vsignal(test)),'r-x',... f(test),abs(Vsignal(test)),'g-');grid on; xlabel('F, Frequency, Hz');ylabel('V, Volts/Hz'); % Total with noise figure;plot(f(test),real(V(test)),'b-o',... f(test),imag(V(test)),'r-x',... f(test),abs(V(test)),'g-');grid on; xlabel('F, Frequency, Hz');ylabel('V, Volts/Hz'); % Plot in dB on a wider frequency scale test=find(abs(f)<20*max(f1,f2)); figure;plot(f(test),20*log10(abs(V(test))),'g-');grid on; xlabel('F, Frequency, Hz');ylabel('V, dB re 1 Volt/Hz');
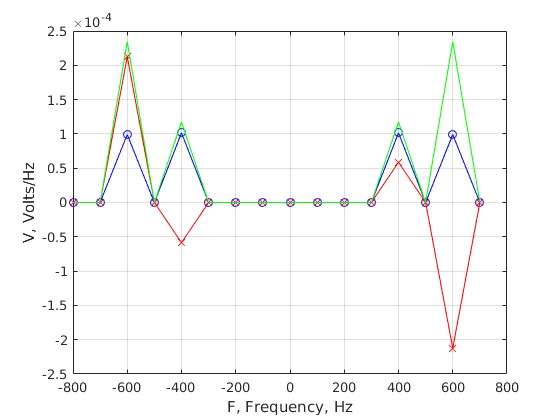
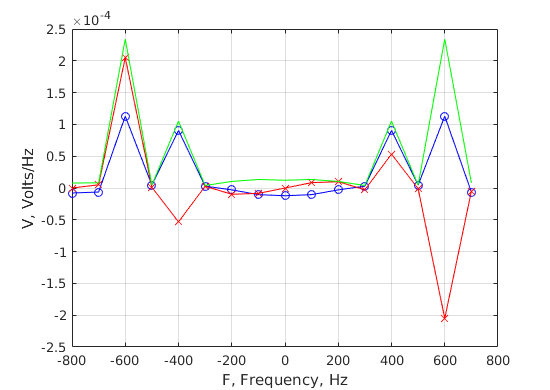
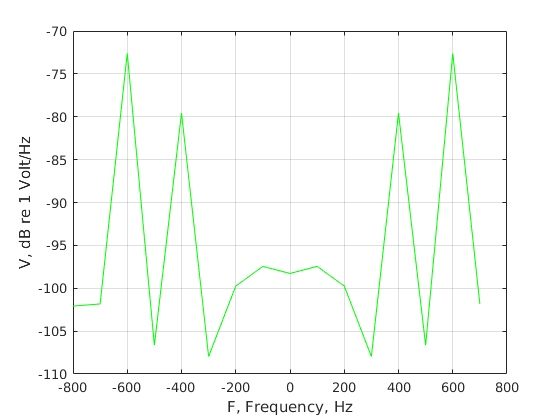
Look at the measurements of the first signal
df=1/max(t); signalamplitude=[vm1,vm2] signalphase=[phi1,phi2]*180/pi fpk=find((abs(f)==f1)|(abs(f)==f2)); freqency=f(fpk) measuredamplitude=abs(V(fpk))*df measuredphase=angle(V(fpk))*180/pi
signalamplitude =
0.0250 0.0500
signalphase =
30.0000 65.0000
freqency =
-400 400
measuredamplitude =
0.0112 0.0112
measuredphase =
-30.4785 30.4785